Page Contents Table
The standard mileage rate makes sure that the vehicle moves according to the assigned offset rate. The taxpayers and professionals across the United States are obligatory to move their vehicles within the given mileage rate. In 2020, All the automobiles either the business vehicle or the domestic one comes under the umbrella of the IRS Mileage Rate. IRS (Internal Revenue Service) is the only primary junction that sets the mileage rates. The Internal Revenue Service’s primary goal is to gather taxes from the public. They are one who is responsible for managing, auditing, analyzing and making sure that no escapes from the net of taxes. IRS has to execute these tasks within the minimum cost. They are also abode by taking care of Public personal data integrity and confidentiality.
Current IRS Standard Mileage Rates 2020 [Holistic View]
The year 2020, has neither witnessed the increase in the mileage rate nor the decrease. By far, we have seen information on the Internet regarding the IRS Mileage Rates for the previous year. This year we are going to publish detailed information regarding the IRS Standard Mileage Rates for the Year 2020 in the United States. By the end of this guide, you will have enough information regarding the mileage rates and you by yourself will be able to save yourself from getting into any trouble.
2020 IRS Mileage Rate
Reimbursement
-
IRS Mileage reimbursement rates
-
- The year 2020 IRS Mileage reimbursement rate is 57.5. We have seen a slight decrease in the rate as compared to the previous year 2019.
-
-
Calculation
-
-
Things to consider before diving into the calculation of IRS Mileage reimbursement.
- Mileage (Business, Medical, Charitable)
- Reimbursement rate (the current year is 2020)
-
-
-
-
-
- IRS mileage reimbursement calculator
- FORMULA = TOTAL MILEAGE X CURRENT REIMBURSEMENT RATE
- IRS mileage reimbursement calculator
-
-
-
Commute rules
- Many people are unaware of the commute rules the IRS has. They are obligatory for all types of vehicle owners. The circumstances change every year and you without even knowing could get a tax deduction for commuting.
-
Introduction to IRS Commute
- IRS has a predefined definition of what does commute means. It is regarded as the transportation in your usage within the parameter of your home to work or vice versa.
-
Things to know before getting into the hullaballoo
- If you are going on the trip between your home and your main or primary workplace or job and vice verse. These charges will never be deducted.
- In case if your route is between your home and the temporary workplace (that is not mentioned in the IRS records). Then you might face deduction. Because you are permitted to go to the place which is mentioned in the IRS databases.
- The commute will not be taken away if you are doing a part-time job. You could go to the second job from home or from your primary job and return back to the corresponding locations without any headache of deduction.
- The regular or primary job trip to the temporary job is bound to deduct your commute according to IRS rules.
- You can eliminate routes that come in the net of your major job and temporary one.
- You are permissible to deduct drives between a temporary workplace and a secondary job
- We may witness many commute-based drives turning into business-driven routes that is a deductible home office.
-
Commute rules that are tax-deductible
- The tax deduction occurs when the traveling route is between the home and temporary workplace.
- The travel for domestic purposes unlike emergency to hospitals is deductible.
-
- IRS has a predefined definition of what does commute means. It is regarded as the transportation in your usage within the parameter of your home to work or vice versa.
-
Rules for employees
- IRS mileage reimbursement rules for employees are as follows:
-
-
- The amount that must be included in the employee’s income and wages for the personal use of an employer-provided automobile generally is determined by reference to the automobile’s FMV
- An employee lives in Flordia and has a workplace within Florida. He is asked to come to Texas for an office or business meeting, the tax is not deductible for him.
- An employee resides in Texas and goes to the meeting in Texas, he is bound to pay Tax.
-
-
Rules for employers
- IRS mileage reimbursement rules for employers are as follows:
- The employer is the one who can prove business-driven traveling routes and other entertainment or extra charges must be submitted weekly in the report. Also, the invoices and necessary receipts must be attached to the report.
- The employer is obliged to exclude employee’s wages reimbursements of the entire business expenses that are deductible. These rules must be followed under the umbrella of arrangement.
- The employer also reimburses nondeductible business expenses (such as travel not away from home) and treats those reimbursements as wages.
- The employer must not reimburse its current employees for their personal expenses. The employee must bear his extra expenses on his own.
- IRS mileage reimbursement rules for employers are as follows:
Allowance
Following are the current IRS mileage allowance rate:
-
Business Purpose IRS Mileage Allowance Rate for 2020
- 57.5 cents per mile for business miles driven.
-
Medical or Emergency or Moving Purpose IRS Mileage Allowance Rate for 2020
- 17 cents per mile driven for medical or moving purposes.
-
Welfare or Charitable purpose IRS Mileage Allowance Rate for 2020
- 14 cents per mile driven in service of charitable organizations.
Deduction / Depreciation
-
IRS mileage deduction/depreciation rate for 2020
- Deduction from 58% to 57.5% for business-driven vehicles.
- Deduction from 20% to 17% for medical purpose vehicles.
- The charitable section remained the same. 14 % was in 2019 and is still 14% in 2020.
Form
- IRS mileage form needs to be filled to avail the opportunity.
Guidelines
There are a few guidelines that need to be followed:
IRS Guidelines
-
- Store the entire log of the mileage of traveling for business-related purposes. The business-based may include driving from home to primary office, visiting clients, driving to the offices of small business holders. These all generate a hefty amount of direct income through tax assigned by the IRS.
- Make sure you use only five vehicles, more than five vehicles operating within the business and also at the same time could trigger the IRS. Also, make sure that you do not use any business-related transport or vehicle to carry a person or business-related entity in order to redeem compensation. In case, you happen to claim Section 179 regarding depreciation and deduction, then you will not be allowed to use the standard mileage rate until the issue is resolved by the IRS.
- Claim a deduction using the standard mileage rate in the first year the vehicle is available for business use. Once you do so, you can switch from using the standard mileage rate to deducting actual car expenses in later years. If you have owned the vehicle for more than a year and did not take a deduction based on the standard mileage rate in the past, you are no longer eligible to use the standard mileage rate. Small-business owners and other self-employed workers can claim the deduction by filing Form 1040, Schedule C, while employees who use personal vehicles for business purposes can use Form 2106.
Business
Business-driven vehicles are for the purpose of assisting the employees for business tours. But if you are a self business person and owns some small business, then you must abide by the rules of IRS Small business owners guide.
-
Current IRS Business standard mileage rate
- The expense of driving a car for business purposes (not commuting or other personal use) is a legitimate business expense, and you can deduct these expenses on your business tax return
- The current IRS Business vehicle mileage rate for the year 2020 is:
- 57.5%
Standard
- The current business-standard mileage rate is 57.5% per mile.
- The current IRS standard mileage rate for 2020 is 57.5%
- The federal standard mileage rate is 57.5% per mile.
- The standard mileage rate for charitable purposes is 14%
Charitable
The charitable organizations that are purely based on developing public infrastructure and public safety are eligible for a tax-deductible approach according to Code 170. The organizations must fulfill the requirement to operate in the country as set by the IRS. In contrary to this, those organizations which contain vested and self-interested are exempted from the IRS tax-deductible approach. Also if the organization holder is a private individual and all share holder’s assets exceed the limits of the transaction as set by IRS, then they must report back to the IRS. If the organization key holder has more than enough influence over the organization, then he will also be dealt with strict policies of the IRS. The organizations with the intent of lobbying and doing political activities within the premises of the organization will be dealt with strictly.
-
Pinpoints to note:
- The charitable infrastructure IRS mileage deduction rate for the year 2020 is nearly 14%.
- The charitable mileage rate is expected to decrease in the coming year 2021.
- The standard mileage rate for charitable purposes does not frequently change in the IRS guidebook.
Federal
The mileage rate is the assigned offset rate. The taxpayers and professionals across the United States are obligatory to move their vehicles within the given mileage rate. In 2020, All the automobiles either the business vehicle or the domestic one comes under the umbrella of the IRS Mileage Rate. IRS (Internal Revenue Service) is the only primary junction that sets the mileage rates.
-
Pinpoints to note:
- The federal mileage reimbursement rate of 2020 is 57.5% for business vehicles.
- The federal standard mileage rate saw a slight decrease in 2020 from 58 to 57.5%
-
What is the current federal mileage rate
- 57.4 %
Historical IRS rates chart
IRS has been publishing IRS tax laws since 2011. Over the span of nearly ten years, we have seen fluctuation. The medical moving vehicle rates are the most transitioning one. While the business rates remained steady. The most persistent one was charity-driven vehicle rates. The charity took the most benefit out of it. In 2020, we witnessed a de-escalation in the numbers of all rates except the charity which has been the same since 2012.
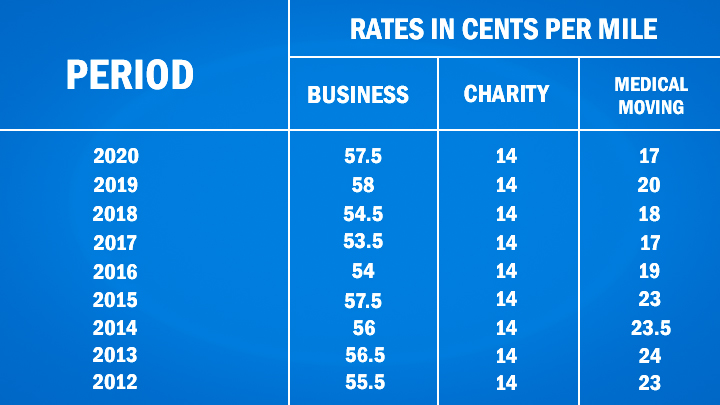
Medical
The IRS standard mileage rates 2020 in the medical area for transportation are solely based on emergency purposes. In case of dire need, the charges might also be not deducted. The primary transportation that is involved in the medical care facilities has separate medical expenses. Following are the scenarios:
- Fees for the bus, taxi, transportation service, train, subway or ambulance. All these actual fares get the exclusion.
- Out-of-pocket expenses for using your own car, or the standard mileage rate.
- The tolls and parking fees in case of out of the city cases.
Personal
IRS standard mileage rates 2020 for personal use. For employer-related vehicles, the maximum fare as per the market value of automobiles and vehicles would be assigned to an employee for personal use in the calendar year 2020. All rates are per mile based.
-
Pinpoints to note:
- IRS’s personal mileage rate is 56.5% for the year 2020.
Interest
The interest rates occur when the individual makes fluctuation in making the payment.
-
Pinpoints to note:
-
- The current IRS interest rate remained the same this year. 5% for overpayments (4% in the case of a corporation); 2.5% for the portion of a corporate overpayment exceeding $10,000; 5% for underpayments; and.






